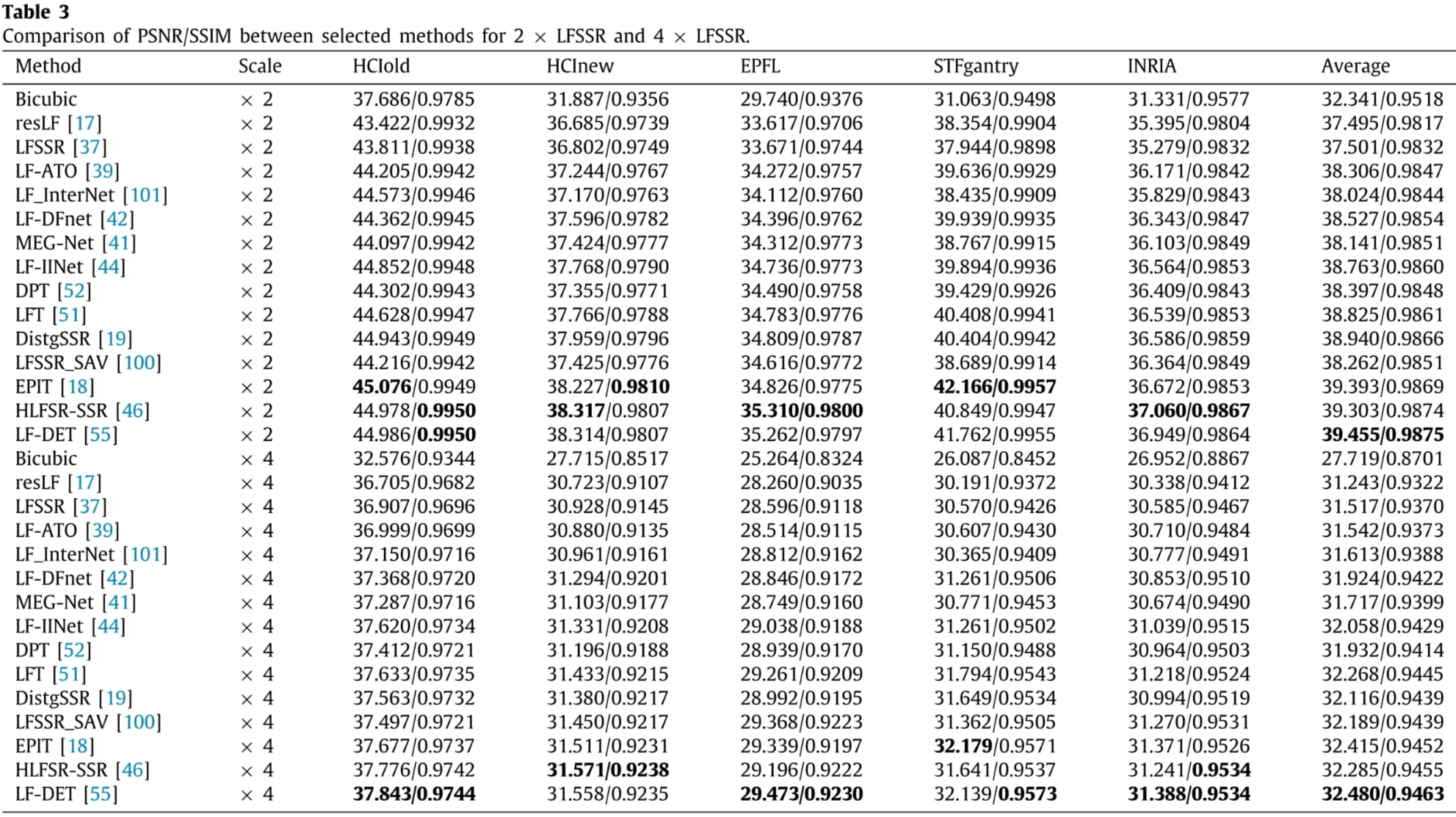
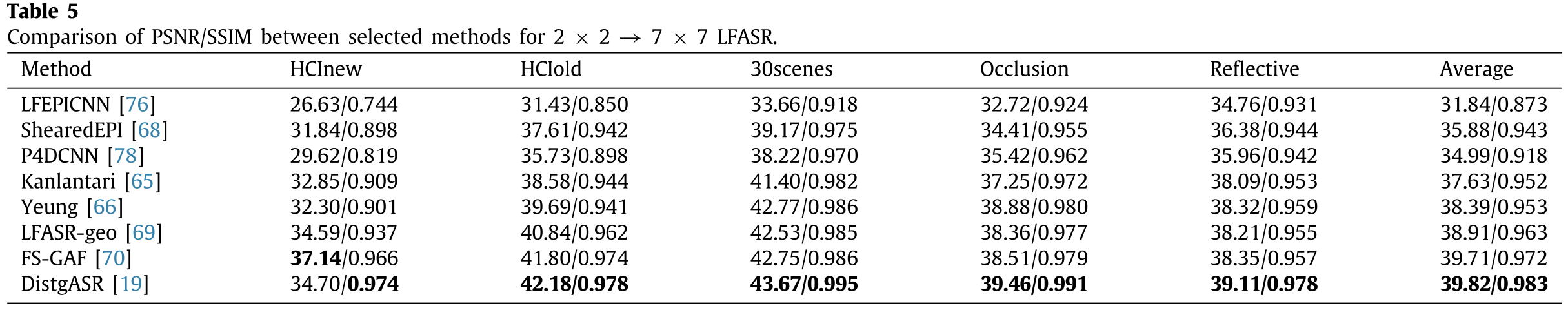
1. Light field spatial super-resolution (LFSSR)
Improve spatial resolution of each sub-aperture image (SAI).
1.1. CNN-based method
Use convolutions to learn spatial / angular correlations and fuse high-frequency details.
- Residual CNNs: Learn directional features and fuse sub-pixel details (e.g., resLF).
- Feature alignment: Optical-flow-based alignment, deformable conv alignment.
- 4D / separable CNNs: Use 4D conv or spatial–angular separable conv to jointly extract features.
- View fusion models: “All-to-One”, multi-view complementary information fusion.
- Attention-based CNNs: Channel/view attention, angular deformable alignment.
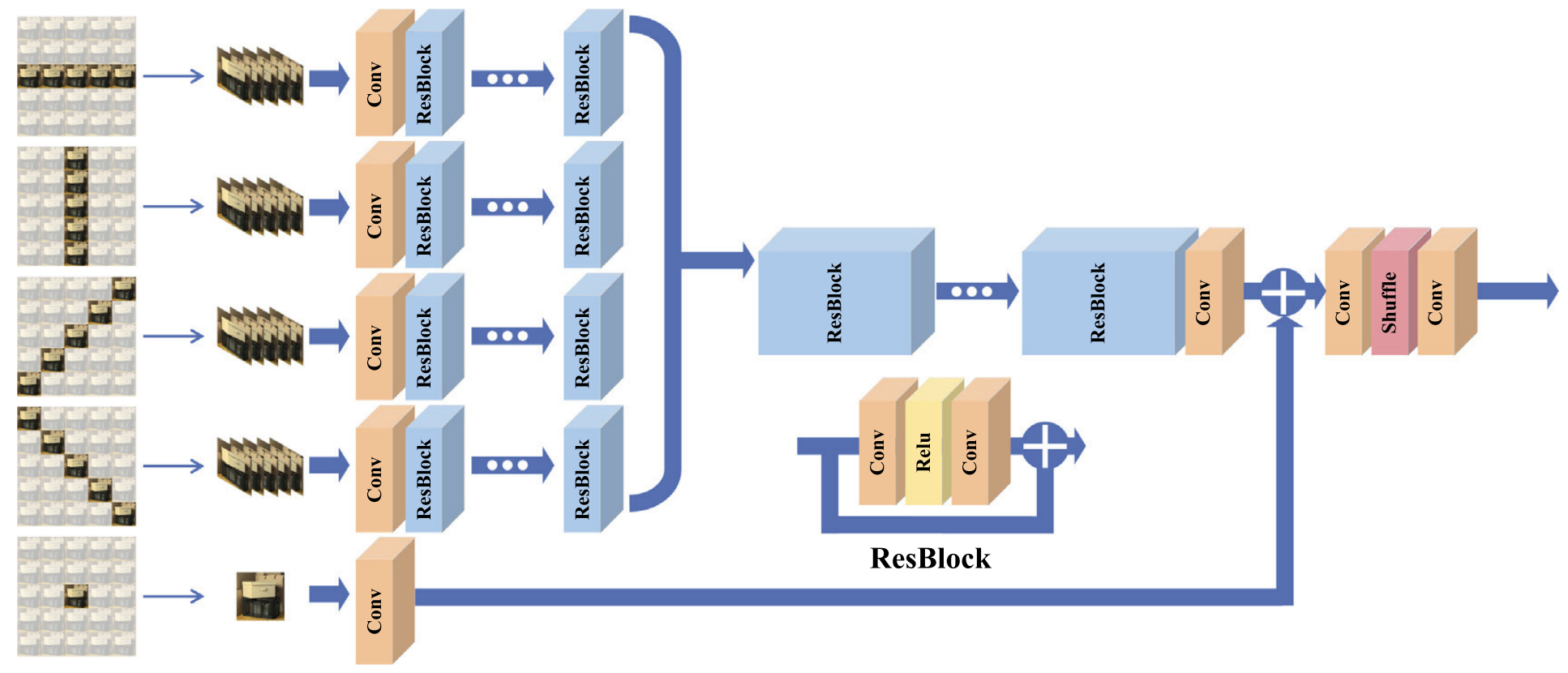
resLF
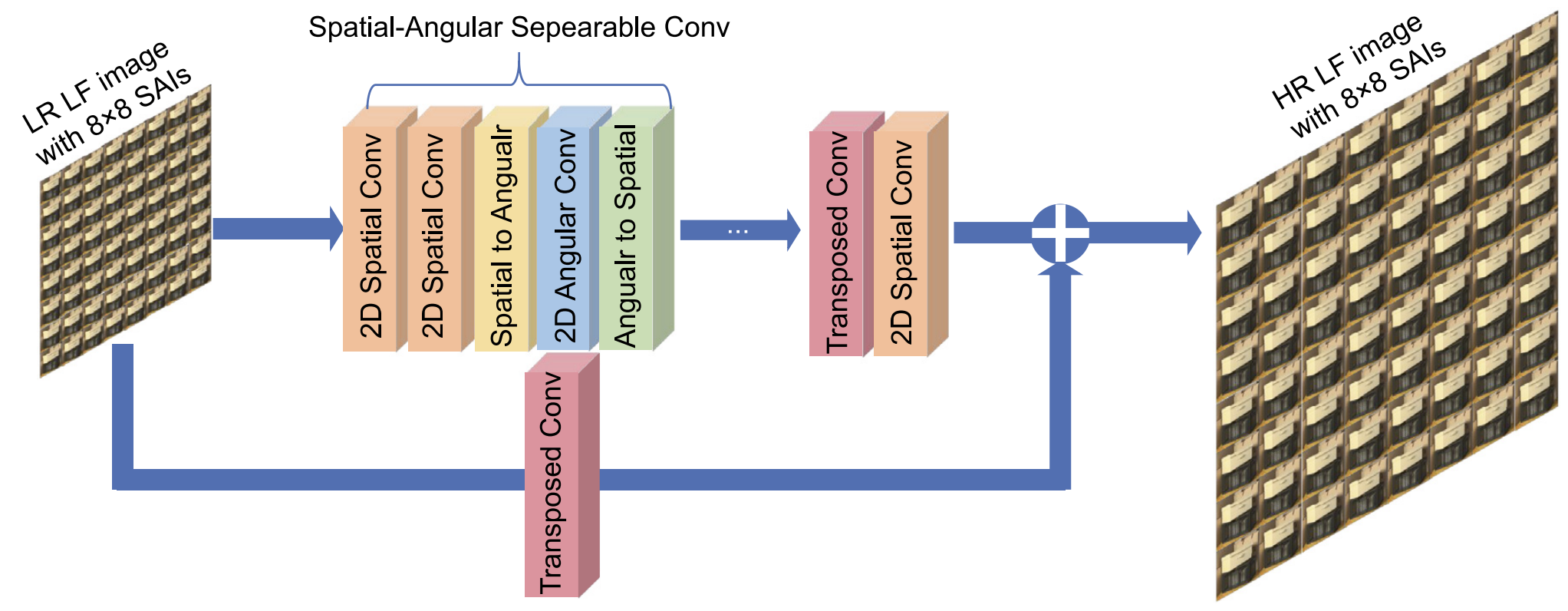
seperable Conv model
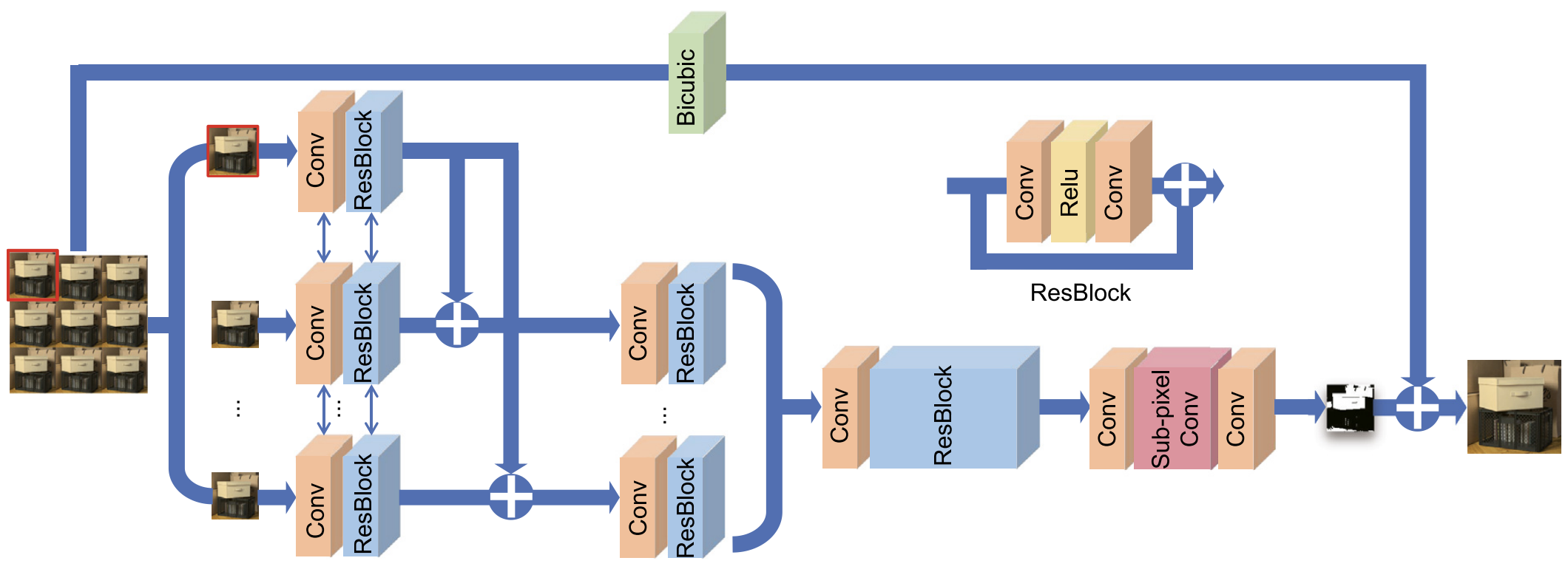
“All-to-One” model
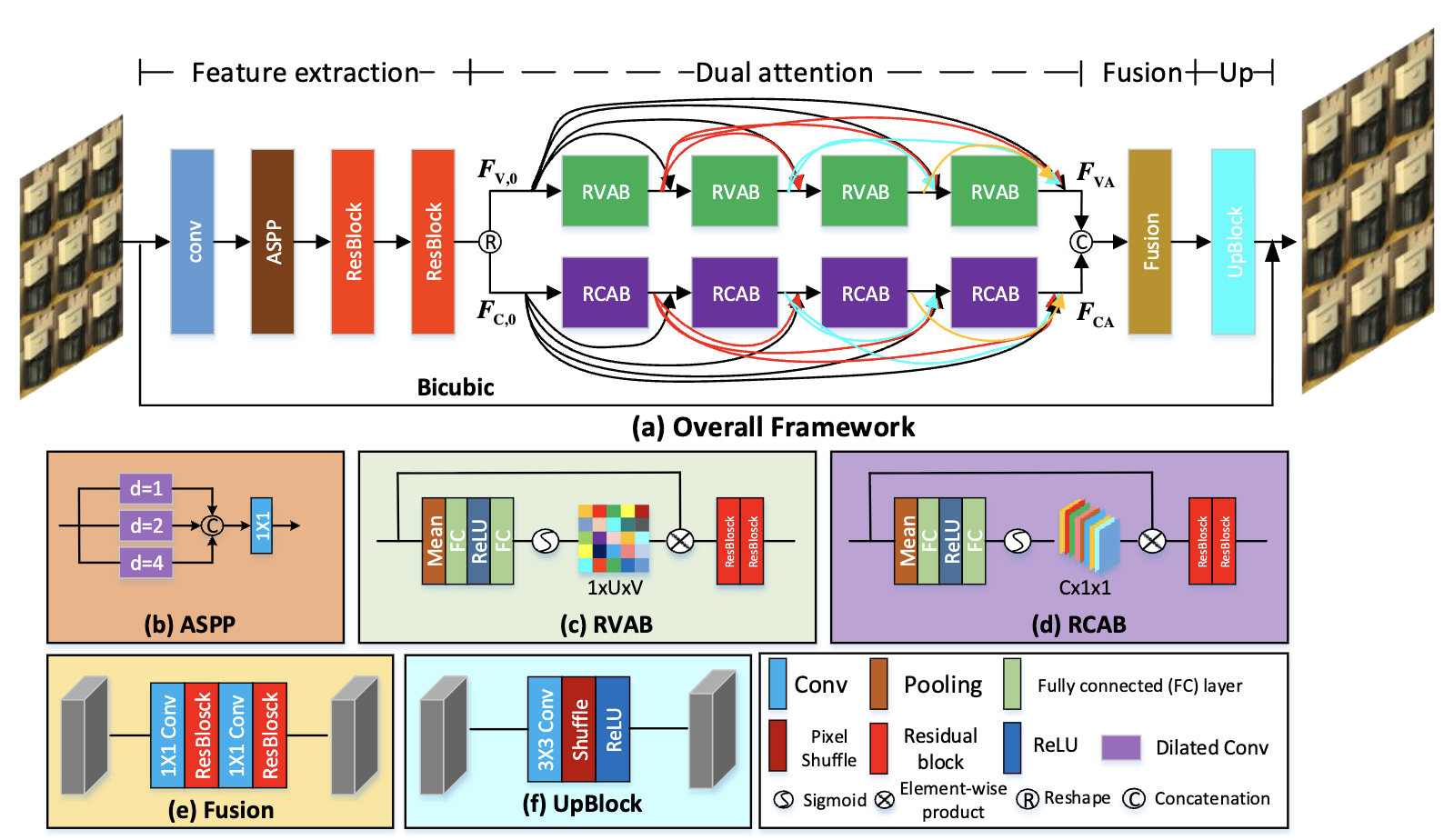
view+channel attention model
1.2. Transformer-based method
Use attention to model long-range spatial-angular dependency.
- Spatial–angular transformer: Self-attention along EPI lines to capture parallax geometry.
- Volume and cross-view transformers: Model correlations across many viewpoints.
- Multi-scale angular transformer: Robust to disparity variations.
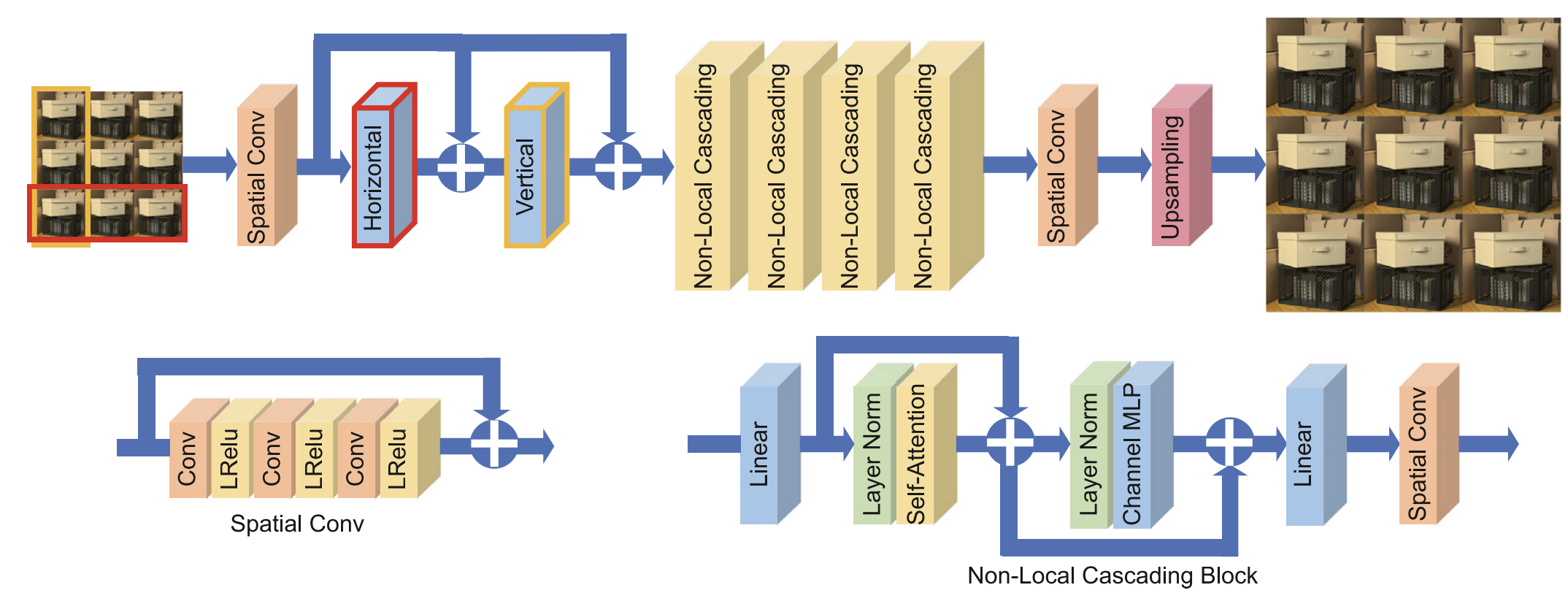
EPI attention
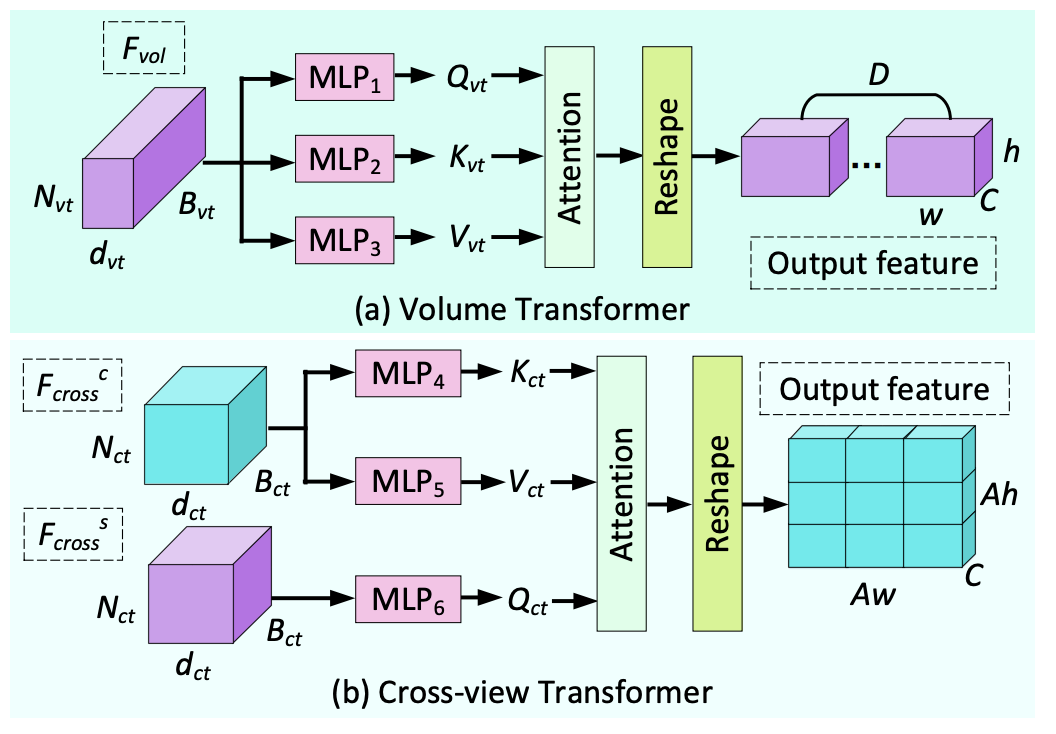
volume transformer and cross-view transformer
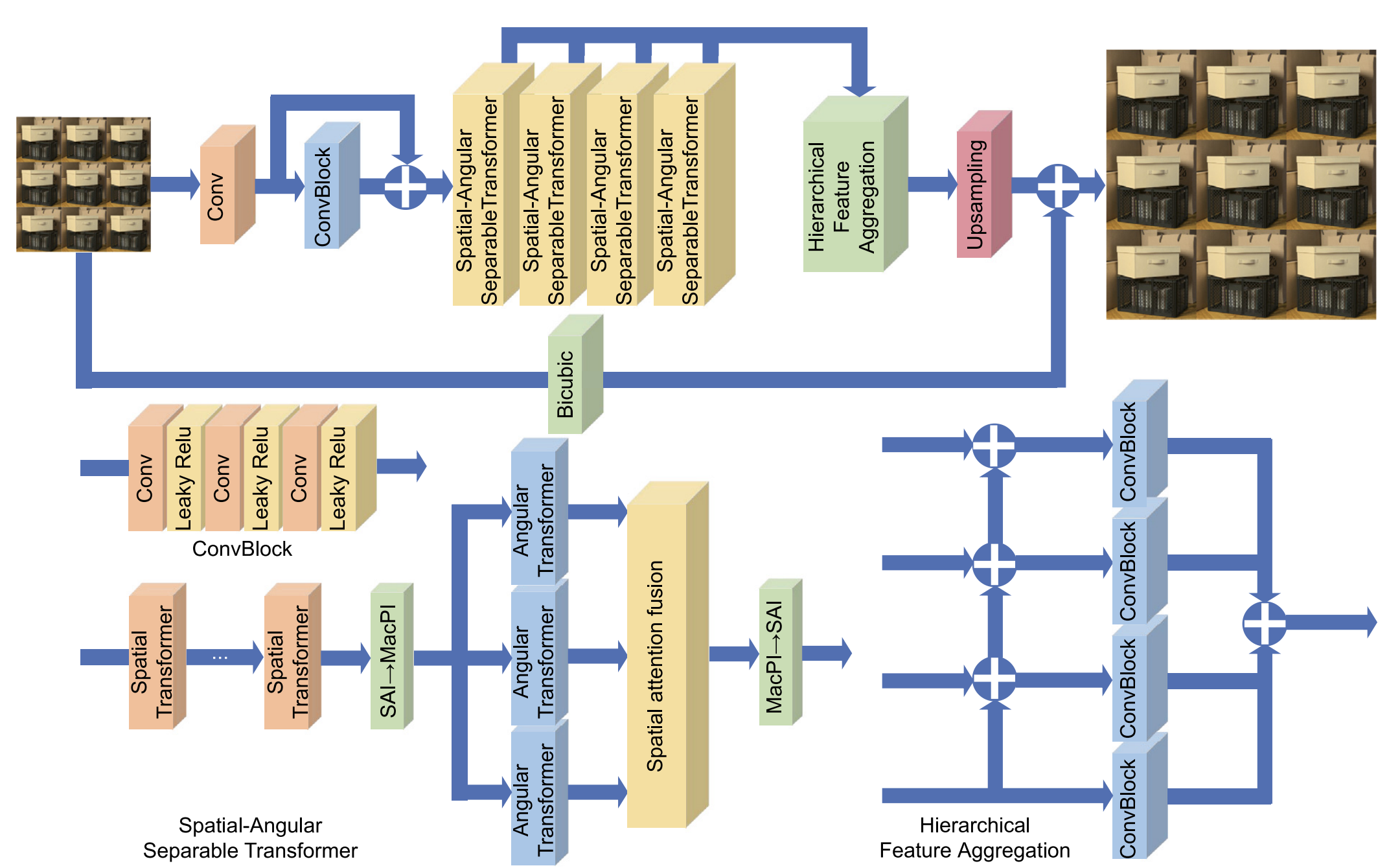
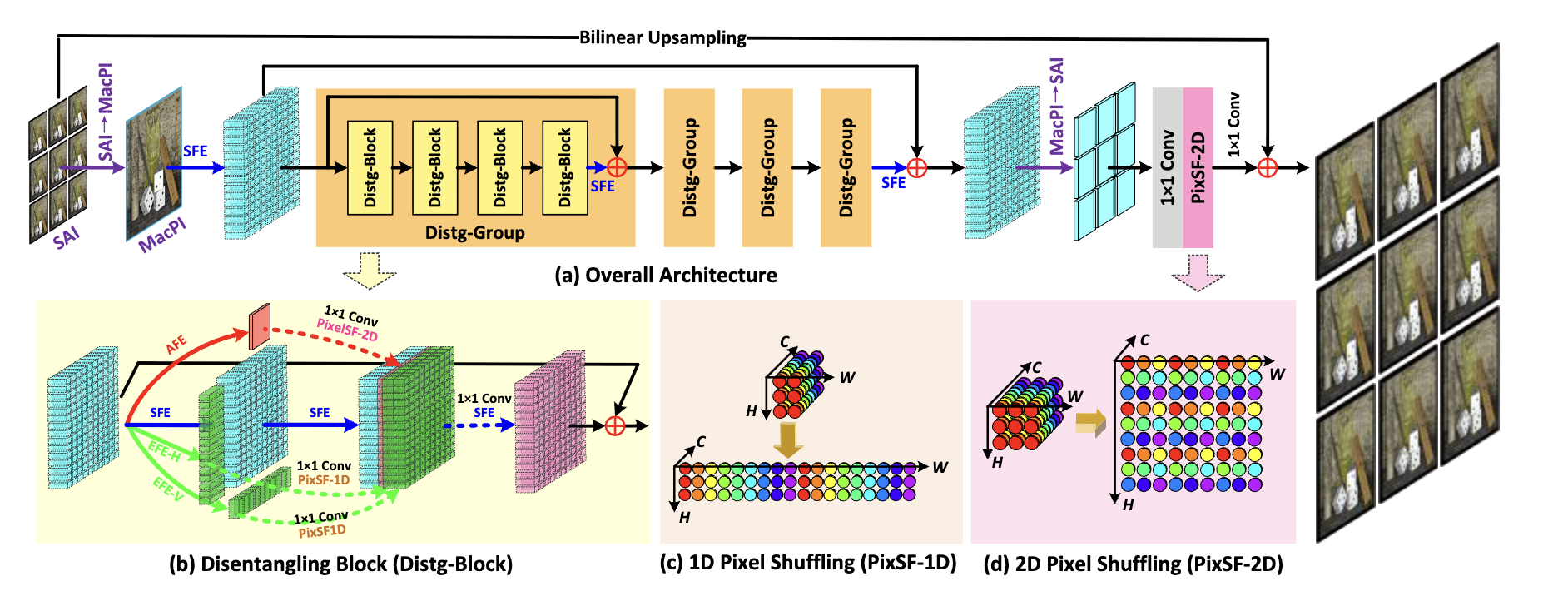
LF-DET
2. Light field angular super-resolution (LFASR)
Increase number of viewpoints (more SAIs) while preserving geometry.
2.1. Depth-dependent method
Estimate depth/disparity → warp existing views → blend new views.
- Optical-flow and superpixel-based warping
- Layered depth representations
- EPI-based geometry modeling
- Depth-guided warping with occlusion reasoning
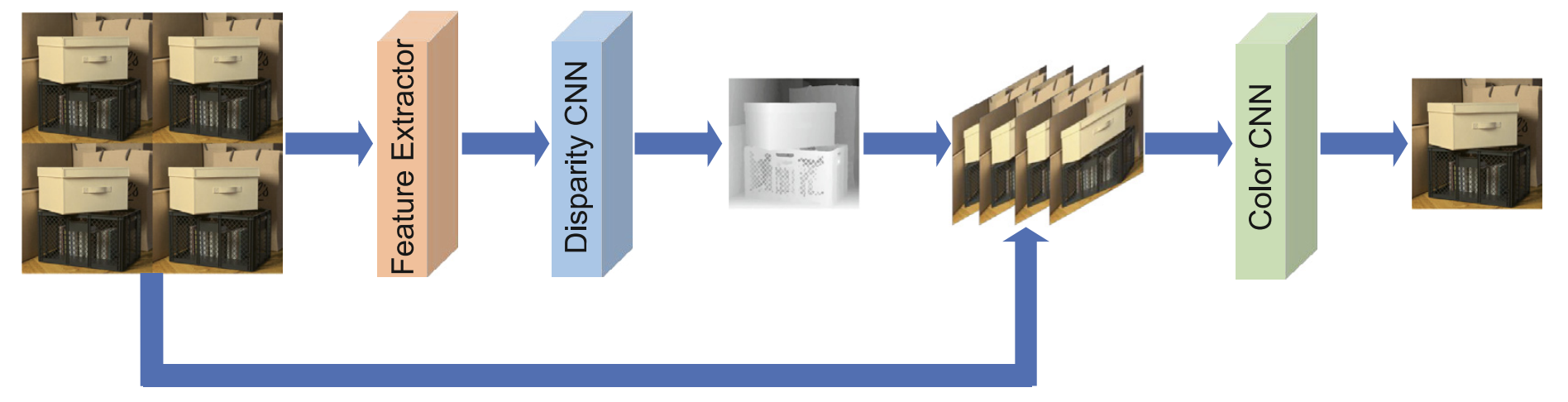
2.2. Depth-independent method
Avoid explicit depth; rely on signal priors or learning-based angular patterns.
- CNN-based angular detail restoration (on EPIs)
- Angular attention models to reconstruct views
3. Light field spatial-angular super-resolution (LFSASR)
Simultaneously increase both spatial and angular resolution → full 4D reconstruction.
3.1. Deep learning-based method
Jointly model 4D light field structure (geometry + appearance).
- 4D CNN encoder–decoder
- Pseudo-4D convolution combining EPI + spatial-angular blocks
- Disentangled models: separate spatial and angular subspaces
- EPI-based networks (CNN + LSTM) preserving geometry
- Self-supervised or domain-generalized models for wild light fields
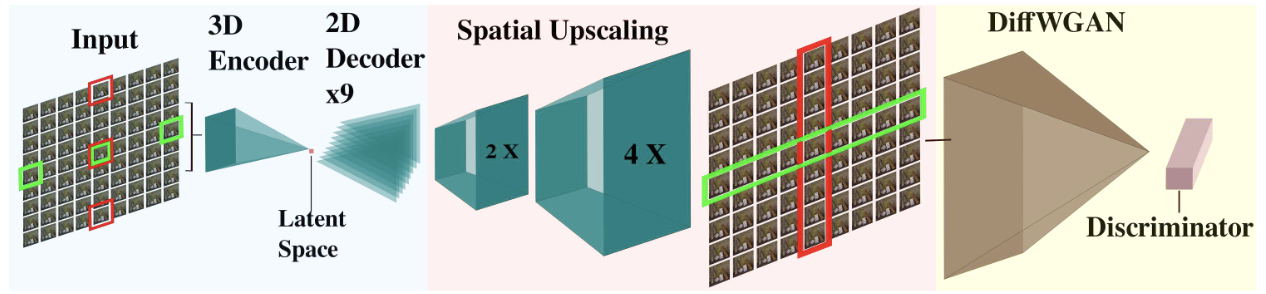
3D encoder
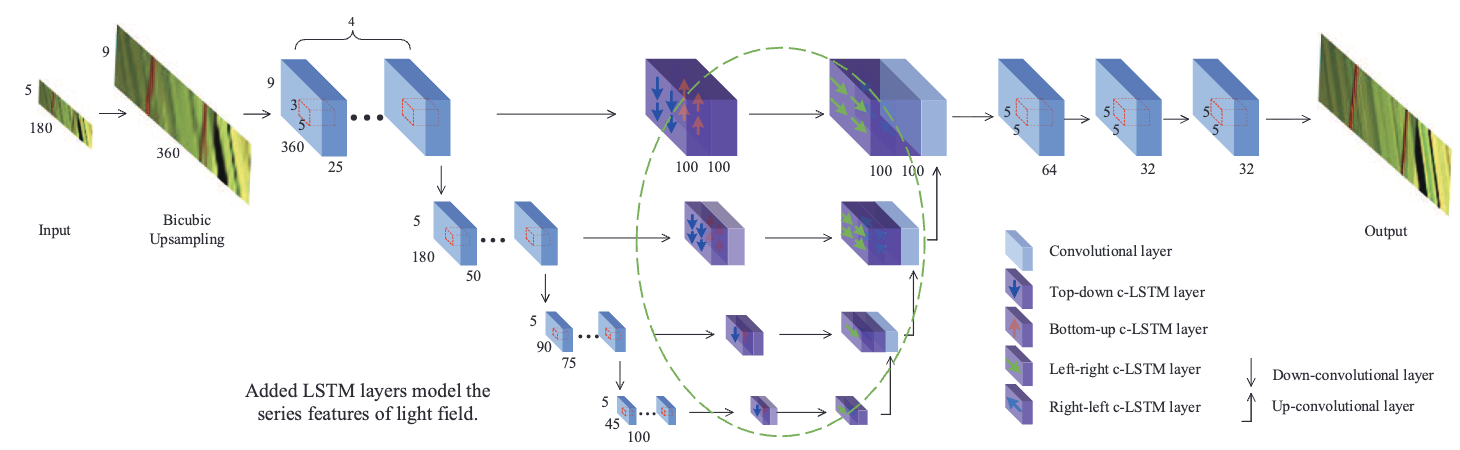
EPI-based networks
Experiments