Review Transformer
Attention in a Transformer takes a sequence of tokens and, for each token, creates a new representation by mixing information from all tokens.
Each token first computes its own query, while every token also has a key and a value. For a token i, attention computes similarity scores between its query $Q_i$ and all keys $K_j$, applies softmax to turn these scores into weights, and then forms the output $y_i$ as a weighted sum of all values $V_j$.
1. Introduction
Traditional attention is expressive but computationally expensive.
Hyena asks:
Can we reproduce the essential capabilities of attention: global mixing + data control —without building a full N×N matrix?
The answer is yes, using two cheap primitives:
- Long implicit convolutions (for global token mixing)
- Element-wise gates (for input-dependent weighting)
| Attention action | Hyena replacement |
|---|---|
| Mixed all tokens according to distance & structure (global mixing) | Toeplitz convolution |
| Weighted tokens based on QK / input (data control) | Gating (diagonal matrix) |
Hyena stacks these primitives in a recurrence to approximate the expressiveness of attention at lower cost.
2. Method
The paper presents Hyena, an attention-free building block that replaces Transformers’ attention mechanism using a recurrence of gating and implicitly-parameterized long convolutions.
Factorizing Attention Into Cheap Components:
Self-attention does:
$$ y = softmax(QK^\top) V $$
Hyena replaces the giant attention matrix with a product of Toeplitz (convolution) and diagonal (gating) matrices:
$$ H(u) = D_x^N S_h^N \cdots D_x^2 S_h^2 D_x^1 S_h^1 $$
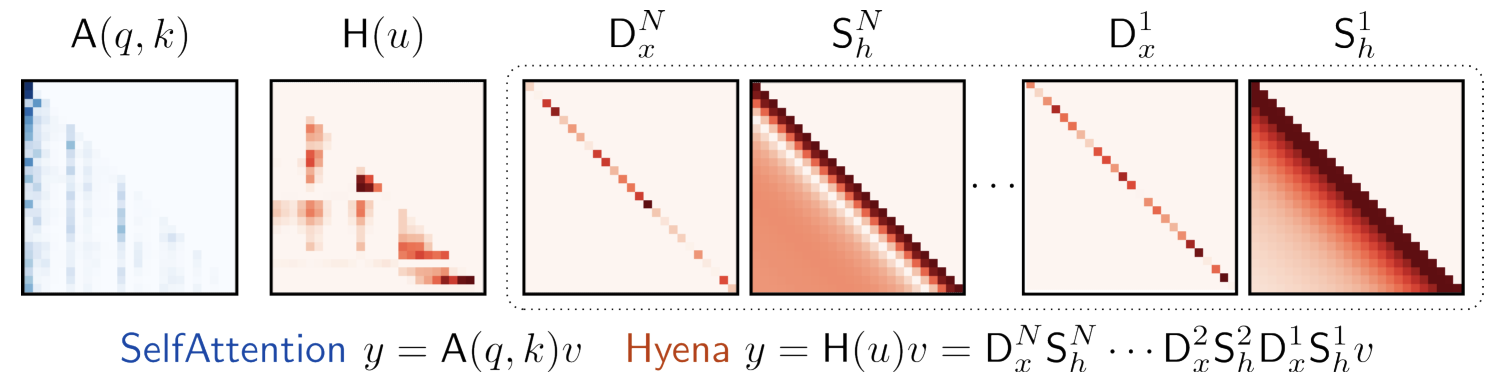
Where:
- Sₕⁿ — Toeplitz matrices implementing long convolution
- Dₓⁿ — diagonal matrices implementing input-controlled gating
Hyena forward pass:

Repeating (conv ➜ gate) N times gives Hyena deep expressive power, similar to attention heads.
3. Novelty
A. Implicit Long Convolutions
Hyena creates very long filters using a small FFN with positional encoding, instead of storing huge kernels. These filters capture long-range dependencies and are applied efficiently with FFT in O(N log N).
$$ h^n(t) = Window(t) \cdot FFN(PosEnc(t)) $$
B. Data-Controlled Gating
Each step computes a gating vector from the input (via a linear layer). This makes the mixing input-dependent, similar to how QKᵀ gives dynamic weights in attention.
$$ v = W_v u \ x^n = Linear_n(u) \ = W_n u $$
C. Recurrence Depth as Multi-Head Analogue
Hyena stacks many (convolution → gate) blocks. Each block learns a different interaction pattern, like an attention head, but sequential and far cheaper.
$$ S_h¹ → D_x¹ → S_h² → D_x² → … → S_hᴺ → D_xᴺ $$
D. Fast FFT-Based Computation
All long convolutions are executed using FFT → multiply → inverse FFT, avoiding large matrices and enabling efficient processing of very long sequences.
$$ h^n * z^n $$
E. Structured Matrix Factorization View
Hyena effectively approximates an attention matrix by breaking it into many Toeplitz (convolution) and diagonal (gating) factors. This yields an expressive, attention-like operator with lower cost.
$$ A(q,k) \approx D_q S_\psi D_k S_\varphi $$