Introduction
AlphaGo
AlphaGo was the first AI to beat top human Go players. AlphaGo combines CNN with MCTS to play Go at a superhuman level.
It first trains two types of networks (policy network & value network & rollout policy), using the current game board combined with several handcrafted Go features as input:
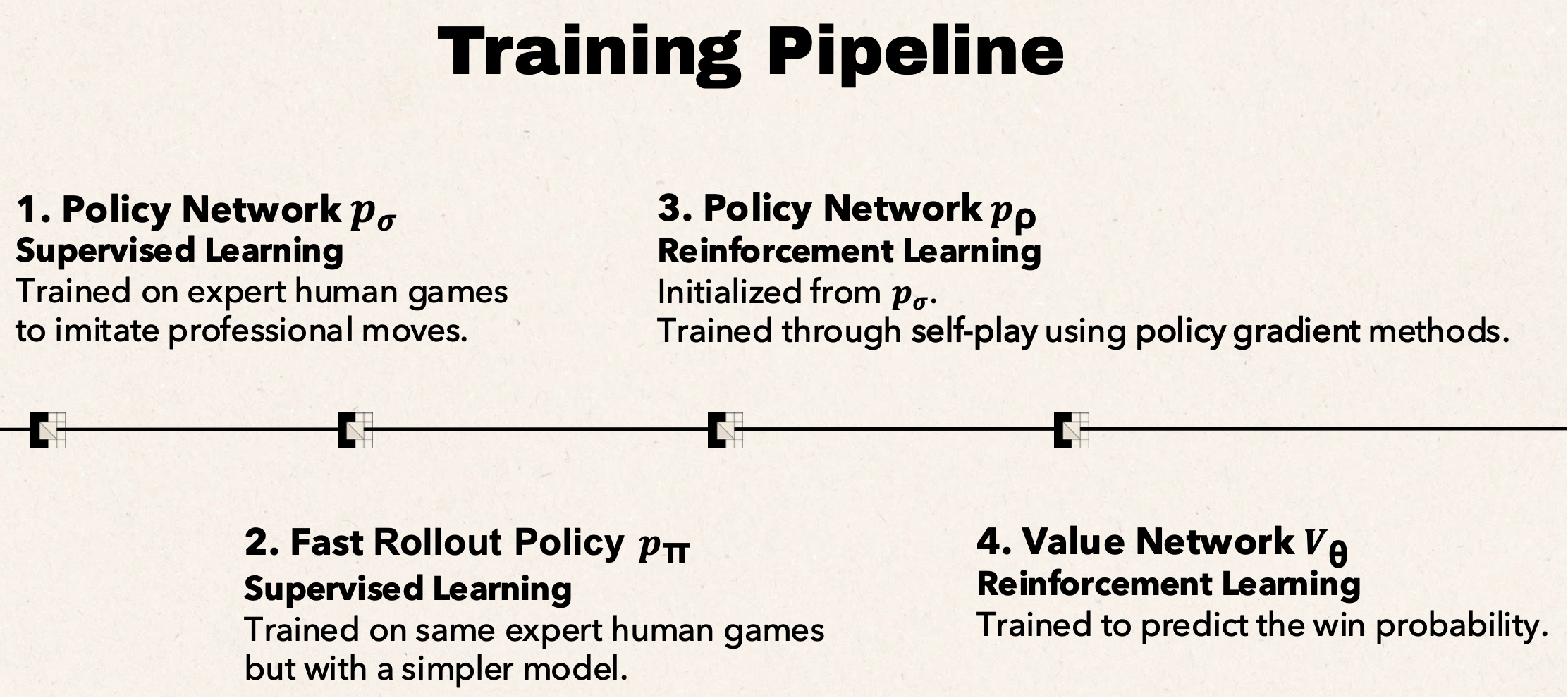
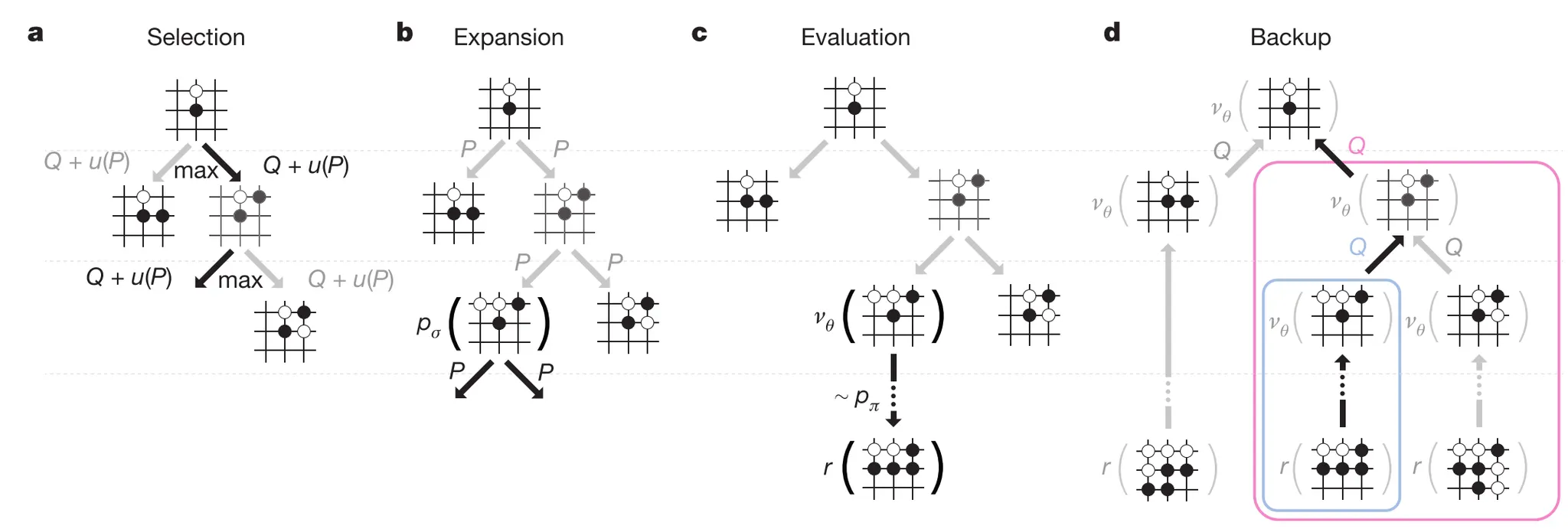
Then integrates the networks into MCTS to enhance the basic tree search.
AlphaGo Zero removes all human input.
- It learns only from self-play and starts from random play.
- Its input is just the raw board (white_stones), with no handcrafted features.
- It uses one unified neural network that outputs both policy and value.
- Its search is simpler (no rollouts) and relies entirely on the neural network.
Method
AlphaGo Zero
Network
The network takes the raw board state and outputs:
- p: a distribution over moves
- v: probability of winning
It is made from deep residual blocks with batch norm and ReLU.
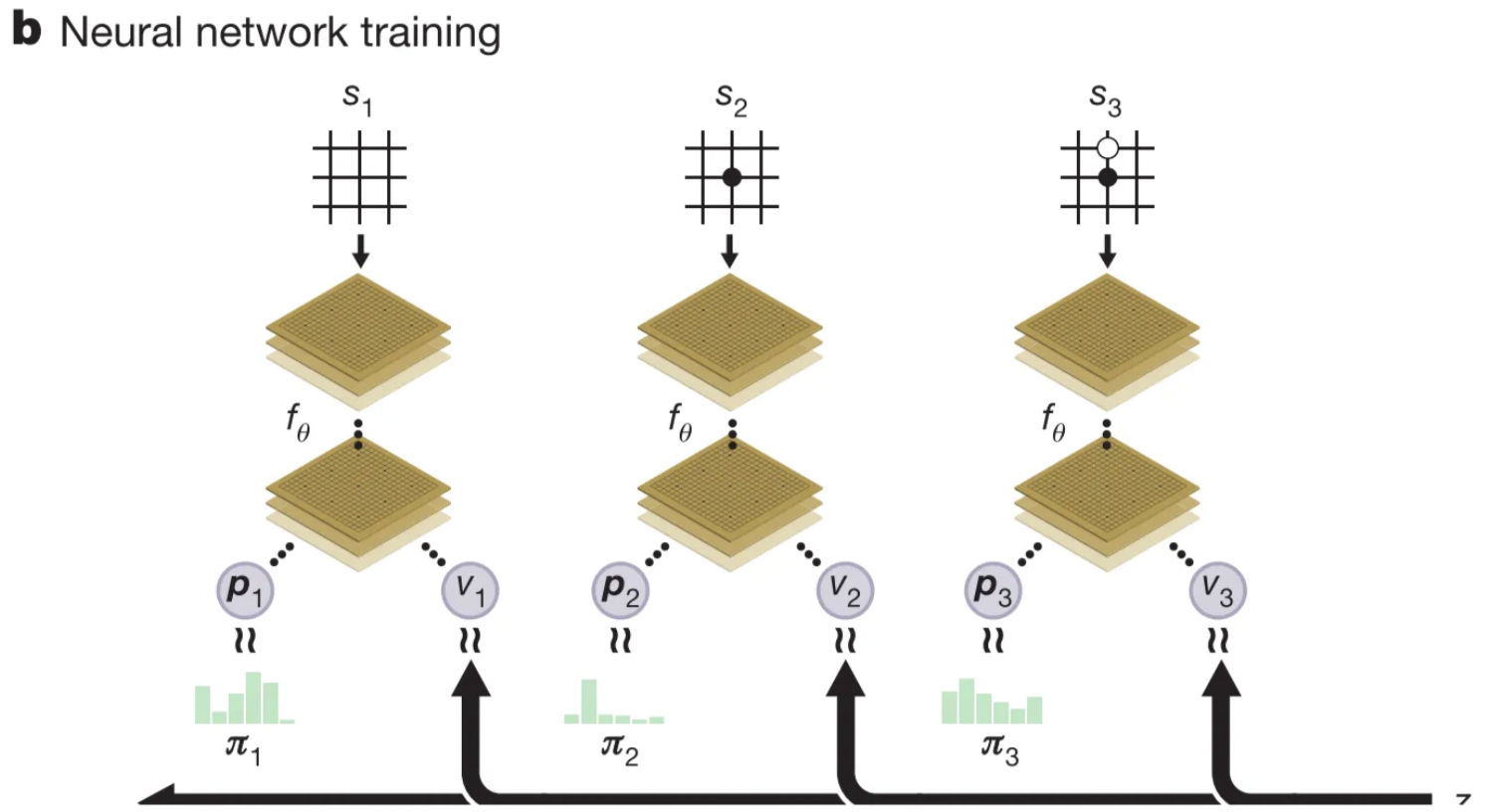
Training the Network
In each training position, MCTS is run using the current network.
MCTS produces an improved move distribution π through simulation like AlphaGo.
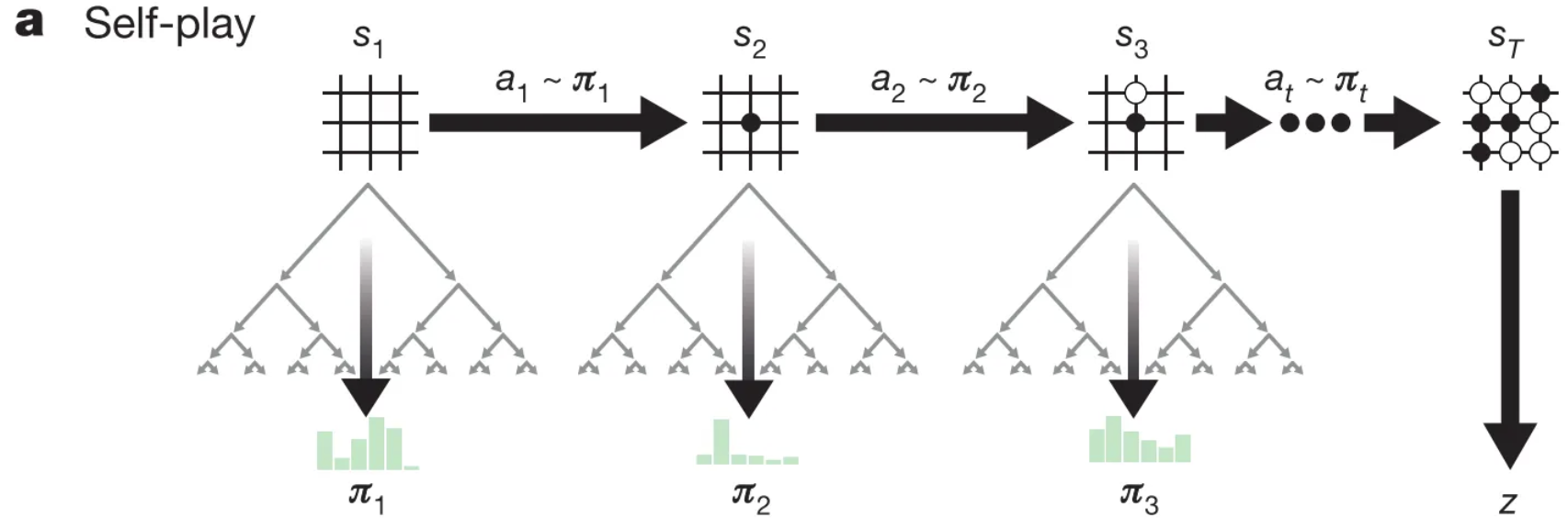
MCTS can therefore be viewed as a policy improvement operator. A new move is selected from π, and the self-play game continues.
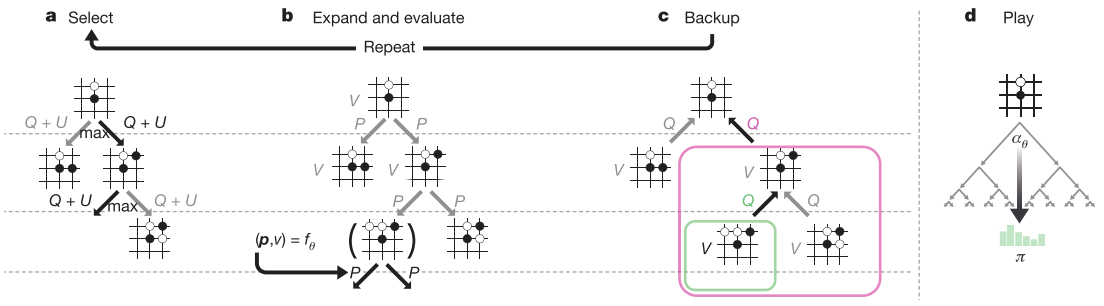
After each game, the terminal result gives a final value z.
Training uses three terms to update the network:
- (z − v)² → match value prediction to the outcome
- −πᵀ log p → match network policy to the MCTS policy
- L2 regularization
Continuous Self-Improvement
AlphaGo Zero repeatedly plays self-play games, updates the network, and replaces the old version when the new model wins enough evaluation games.
Over many iterations, the system improves rapidly and surpasses earlier AlphaGo versions.
Novelty
- It’s trained solely by self-play RL, starting from random play, without any supervision or use of human data.
- It uses only the black and white stones from the board as input features.
- It uses a single neural network, rather than separate policy and value networks.
- It uses a simpler tree search that relies upon this single neural network to evaluate positions and sample moves.