Introduction
- Positional information is very important. Transformers need positional information;
- Old methods add it directly to token representations, making them incompatible with linear self-attention.
Motivation for RoPE:
- Self-attention is often seen as position-agnostic, which is undesirable.
- Attention mechanism cannot understand word order by itself. It does not know the position of tokens.
- Need a method that:
- Encodes both absolute and relative positions
- Works with linear self-attention
- Has good behavior for long-range dependency modeling
→ Previous methods fail at least one of these.
Method
Goal: Encode relative position inside attention
Transformers use self-attention, which computes:
$$ q_m^\top k_n $$
Right now, this inner product does not include position information unless we manually add it.
The authors want:
$$ \langle f_q(x_m, m),\ f_k(x_n, n)\rangle = g(x_m, x_n, m - n) $$
Meaning: the attention score should depend on the relative position (m − n), not the absolute positions m and n.
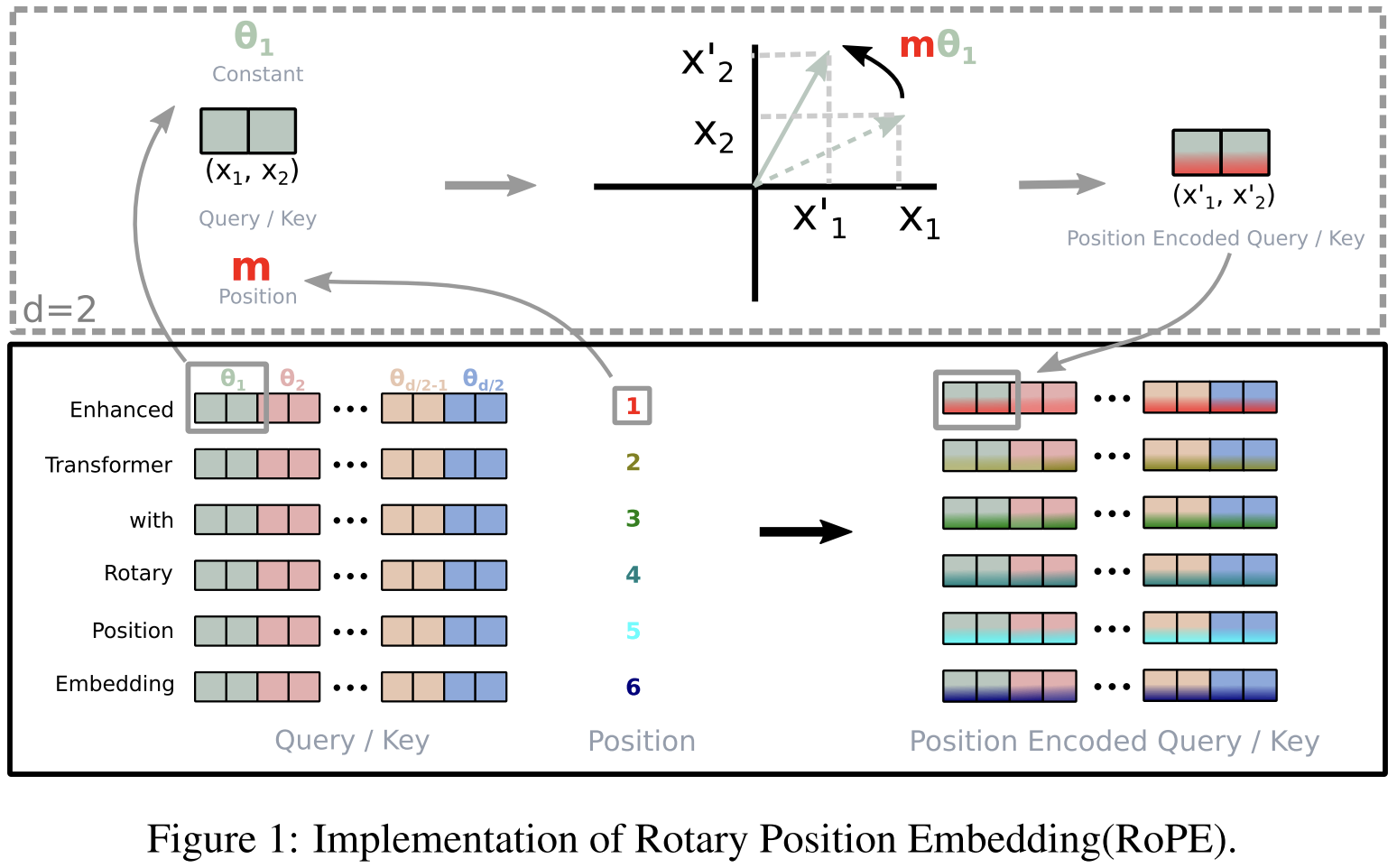
Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE)
RoPE in 2D
Query encoding:
$$ f_q(x_m, m) = (W_q x_m)e^{im\theta} $$
Key encoding:
$$ f_k(x_n, n) = (W_k x_n)e^{in\theta} $$
Here, multiplying by $e^{i m\theta}$ rotates the vector by an angle proportional to position m.
Attention after rotation:
$$ g(x_m, x_n, m-n) = \text{Re}\left[ (W_q x_m)(W_k x_n)^* e^{i(m-n)\theta} \right] $$
Key idea: Rotation angles subtract → giving relative position (m - n).
Real 2D rotation matrix form
Complex rotation can be written as a real 2×2 matrix:
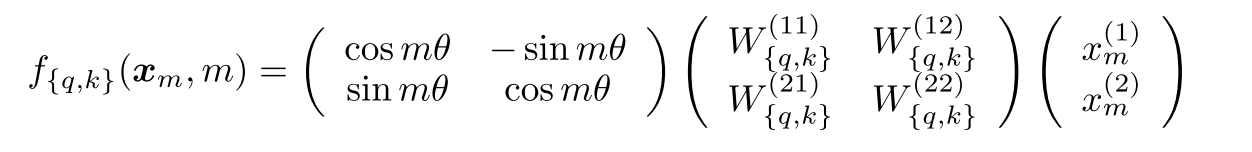
Meaning: A simple 2D rotation based on position index (m).
General RoPE for d-dimensional vectors
Split $x\in R^d$ into d/2 pairs. For each pair, apply a 2D rotation with its own frequency $\theta_i$:
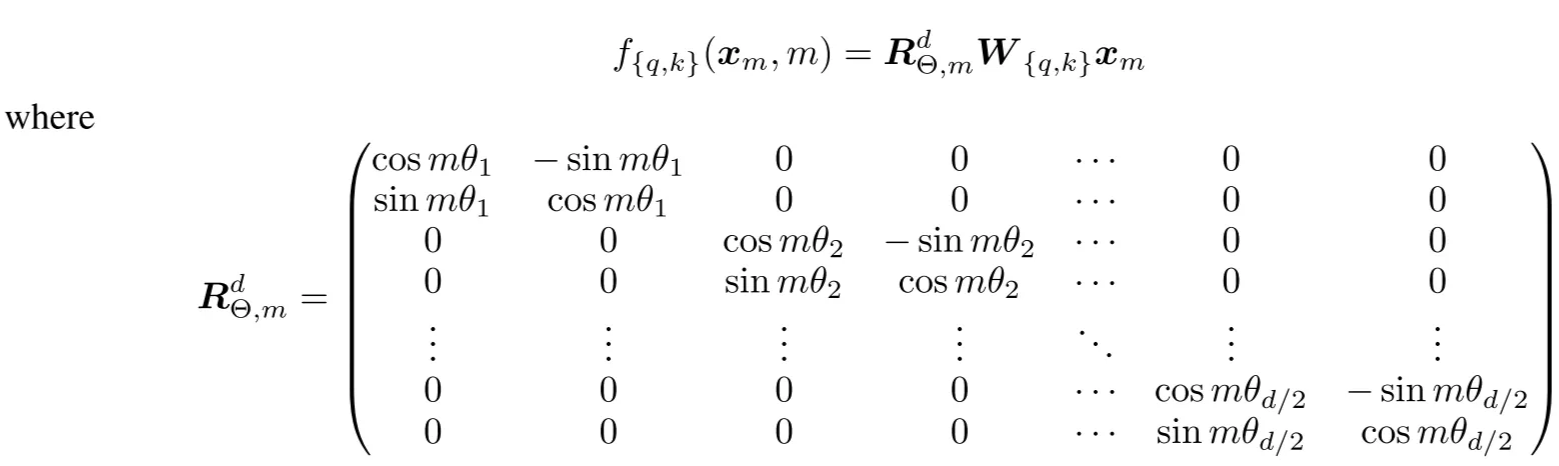
Frequencies:
$$ \theta_i = 10000^{-2(i-1)/d} $$
(same spectrum as sinusoidal PE)
Relative position emerges in attention
Applying RoPE inside attention:
$$ q_m^\top k_n = x_m^\top W_q^\top R^d_{\Theta, n-m} W_k x_n $$
Where:
$$ R^d_{\Theta, n-m} = (R^d_{\Theta,m})^\top R^d_{\Theta,n} $$
Meaning: The effective rotation depends only on relative distance (n - m).
RePE with linear attention
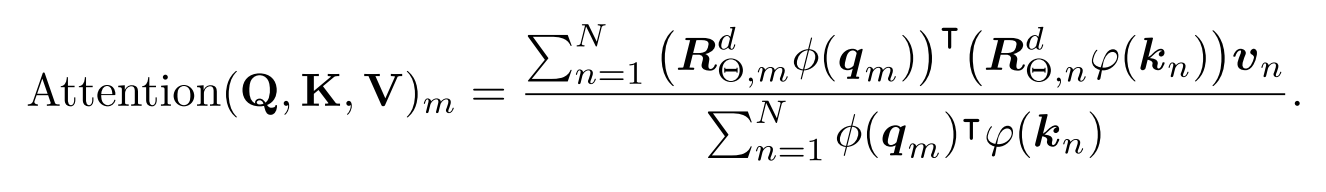
Novelty
- Encode position by rotation, not by adding vectors.
- Relative position appears automatically through angle differences.
- Compatible with linear attention (unlike additive methods).
- No extra parameters; simple and stable.