Github: https://github.com/openvla/openvla
1. Keywords
- End-to-end VLA polic
- Fully open-source (data, code, weights)
2. Problem
OpenVLA is proposed to overcome three major limitations in existing robotic learning systems:
- the lack of end-to-end VLA modeling,
- insufficiently large and diverse robot datasets,
- the reliance on closed-source models and data.
3. Method
3.1. Overall goal
OpenVLA is a vision–language–action (VLA) foundation model that learns an end-to-end robot control policy, mapping visual observations and natural-language instructions directly to robot actions in a closed loop.
3.2. Model architecture
OpenVLA uses a VLM backbone extended for action prediction:
- Visual encoder
- Fuses pretrained features from
- DINOv2 (geometry & structure)
- SigLIP (vision–language alignment)
- Fuses pretrained features from
- Language model backbone
- Llama-2 (7B)
- Receives visual tokens + language instruction tokens
- Outputs action tokens instead of text
This forms a single transformer handling vision, language, and action.
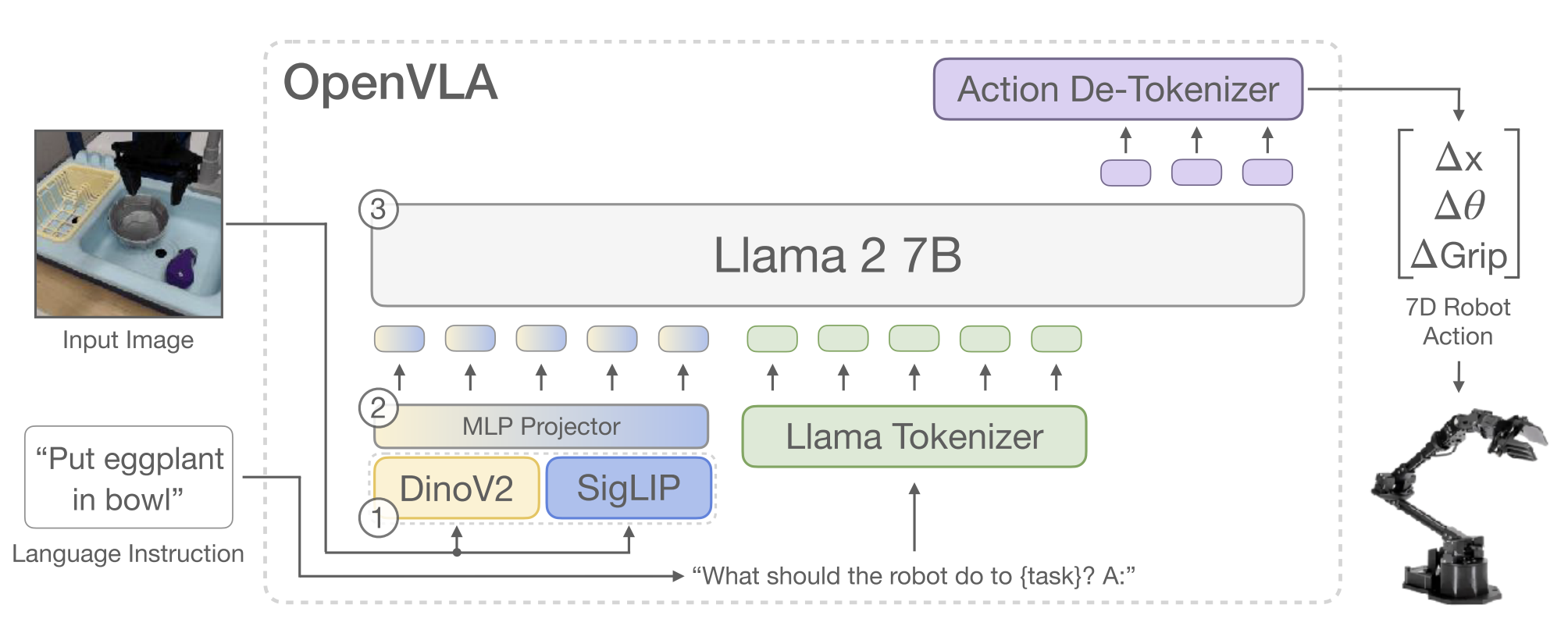
3.3. Action representation (key design choice)
Robot actions are continuous. They are discretized per dimension into 256 bins. Bin ranges are defined using the 1st–99th percentiles of training data → ignores outliers, preserves precision.
Each bin is mapped to a token in the LLM vocabulary, which is implemented by overwriting rarely used tokenizer tokens
Result:
3.4. Training
3.4.1. Training Objective
- Trained using standard next-token prediction
- Loss: cross-entropy
- Evaluated only on action tokens
- No custom control head or regression loss
This allows reuse of pretrained LLM weights without architectural changes.
3.4.2. Training data
- Trained on ~970k robot episodes
- Includes:
- diverse tasks
- multiple robots
- multiple environments
- Episodes are full trajectories (closed-loop interaction)
3.4.3. Inference / deployment
At each timestep:
- Observe camera images
- Read language instruction
- Predict next action tokens
- Decode to continuous control
- Execute on robot
- Repeat (closed-loop control)
One-sentence takeaway
OpenVLA is an open, end-to-end vision–language–action transformer that discretizes robot actions into tokens, enabling a pretrained LLM to directly perform closed-loop robot control at scale.